Table of Contents
When Starlinks SpaceX announced its ambitious Starlinks program in 2015, the tech world stood in awe. The goal? To create a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites providing global high-speed internet access. Fast forward to today, the project has become a groundbreaking yet polarizing initiative, inspiring equal parts admiration and concern.
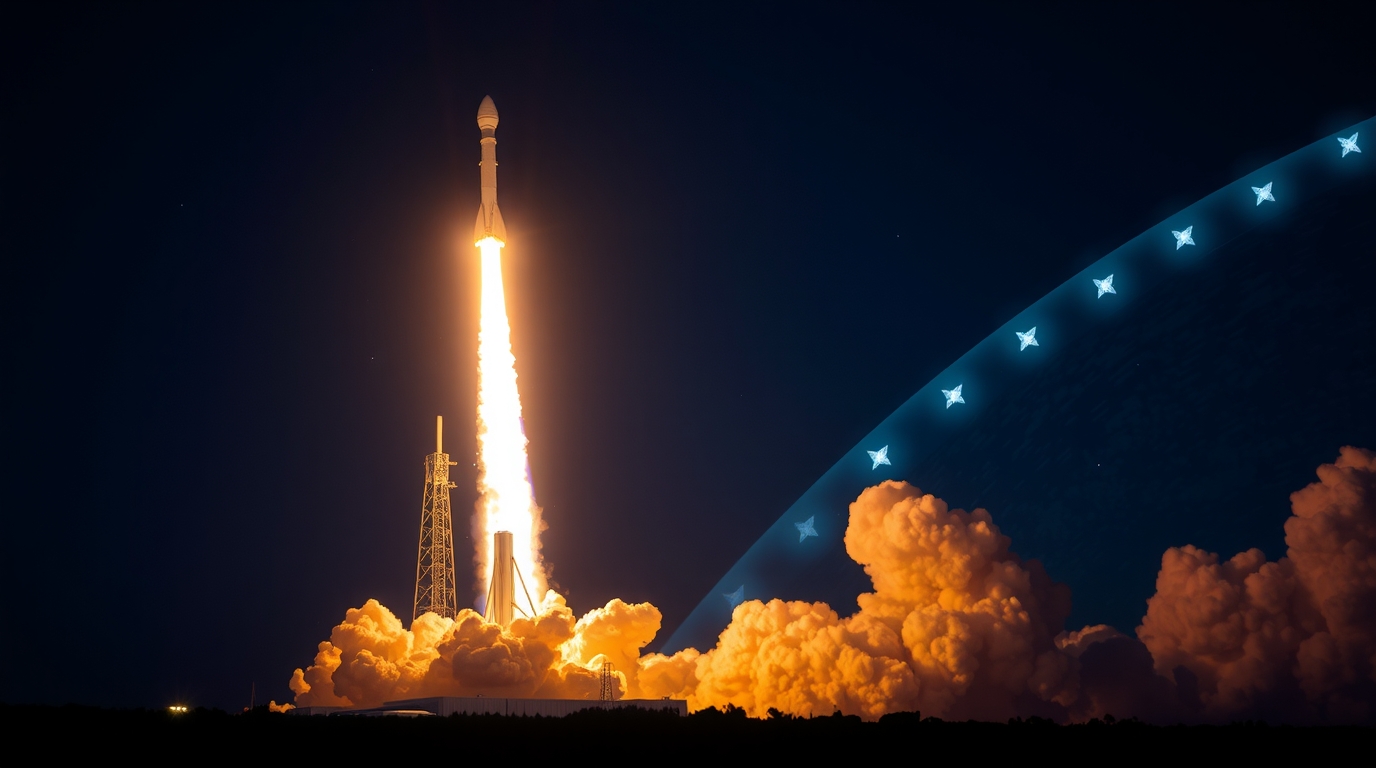
On [launch date], SpaceX successfully deployed 27 additional satellites, ensuring continued momentum toward its mission. However, the project is shrouded in a growing debate over its technical potential, environmental impact, and mounting regulatory challenges. This blog unpacks the recent Starlinks launch, its technological advancements, and the delicate balance between its benefits and the concerns it raises.
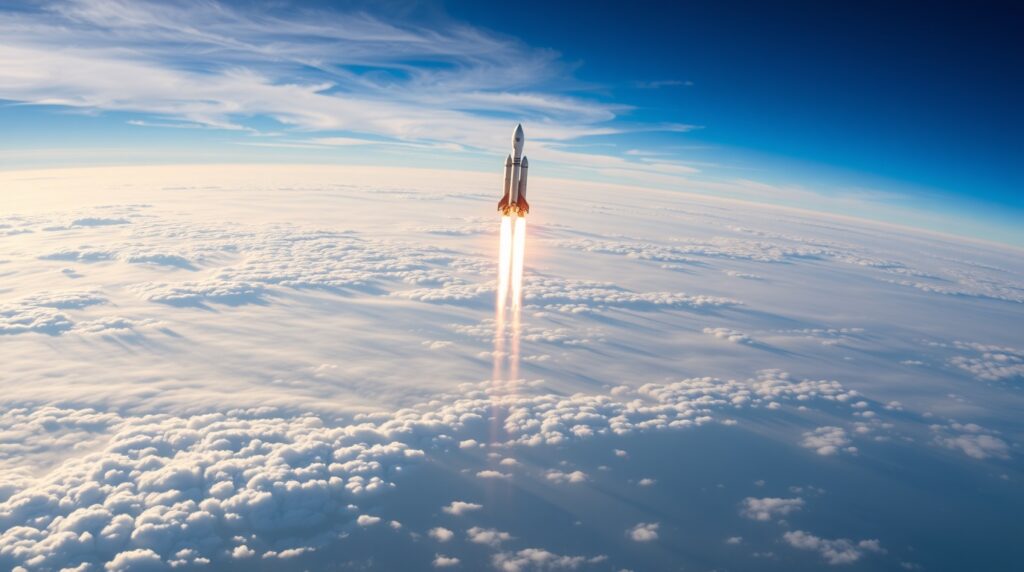

The Recent Launch: 27 New Satellites in Orbit
On [launch date], SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from [launch site], carrying 27 brand-new Starlinks satellite into orbit. This marks yet another key milestone in SpaceX’s aggressive deployment strategy, which aims to establish a fleet of tens of thousands of satellites around the globe.
Shortly after liftoff, the Falcon 9 executed a flawless delivery sequence, releasing the satellites into their designated orbits at an altitude of approximately [orbital destination in km]. True to form, the reusable Falcon 9 rocket returned earthward, landing on its maritime drone ship, “Of Course I Still Love You.” Its efficiency underscores SpaceX’s mastery over orbital logistics.
These new additions bring the Starlinks satellite count above [currently estimated total of active satellites], signaling SpaceX’s relentless push toward a more connected world. But amidst this technical triumph shine lingering concerns that demand attention.
A Peek Under the Hood: Technical Specifications of Starlink
Starlink satellites are marvels of modern engineering, designed to deliver reliable internet to underserved and remote regions. Here’s what makes them cutting-edge:
- Advanced Antennas: Equipped with phased-array antennas, Starlinks satellite can beam internet signals directly to terminals on Earth. This allows them to provide connectivity in hard-to-reach regions.
- Laser Links: Newer Starlinks models incorporate inter-satellite laser links, enabling them to communicate directly with each other. This reduces dependency on ground stations and improves data relay speed.
- Low Latency Advantage: Unlike traditional geostationary satellites, which orbit at 35,786 km above Earth, Starlinks orbit at altitudes between 500 and 1,200 km. This dramatically reduces latency, making it ideal for real-time applications like gaming or video calls.
- Compact and Efficient Design: At approximately [dimension and weight], these satellites pack a lot of functionality into a compact form, maximizing the efficiency of each launch.
Clearly, SpaceX has redefined what we expect from satellite technology. But for all the innovation baked into Starlinks, the service has also raised larger questions about sustainability and ethics.
Benefits of Starlink: A Revolution in Connectivity
Starlink’s promise to decentralize and democratize the internet is nothing short of revolutionary. Here’s why its potential is lauded:
- Connecting the Unconnected: Millions of people in rural and remote regions currently lack reliable internet access. Starlinks could bridge this gap, enabling education, healthcare services, and connectivity in places traditional infrastructure cannot reach.
- Emergency Response: Natural disasters often cripple terrestrial communication networks. Starlink’s portable terminals make it a valuable tool for disaster response teams requiring robust communication under adverse conditions.
- Enhanced Speed and Low Latency: By leveraging LEO orbits, Starlinks provides faster connectivity compared to geostationary options. Customers already report substantial improvements in speeds for streaming, gaming, and video conferencing.
- Economic Opportunities: Starlink’s broadband could empower startups and entrepreneurs in underserved areas, creating new possibilities for local economies.
The social and economic impacts of Starlink could redefine global internet accessibility. But convenience doesn’t come without cost.

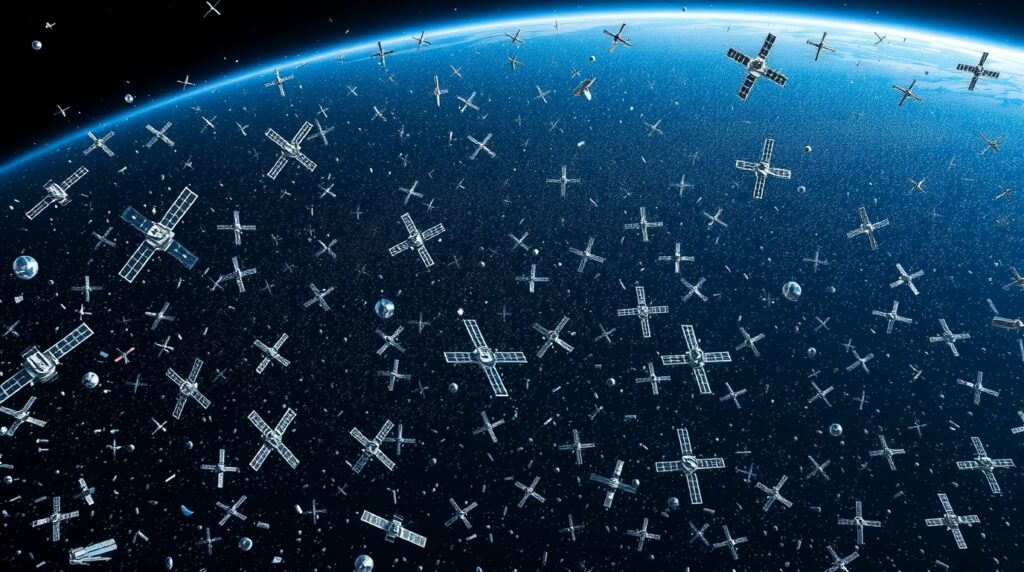
Environmental Concerns Loom Large
While Starlink offers undeniable benefits, the environmental stakes are high. Critics have raised pressing issues about the influx of thousands of satellites into Earth’s orbit:
- Space Debris
With more than [current estimate] satellites in operation, low Earth orbit is becoming increasingly crowded. Decommissioned satellites, collisions, and debris from launches threaten to create a “Kessler Syndrome” scenario, where orbiting fragments make space inaccessible for future endeavors.
- Astronomical Disturbances
Astronomers worldwide have voiced concerns about Starlink’s impact on celestial observations. The reflective surfaces of its satellites interfere with ground-based telescopes, complicating the study of stars and galaxies.
- Light Pollution
Starlink satellites create visible trails in the night sky, altering how we experience the cosmos. The beauty of an unlit sky, key to human curiosity and scientific progress, is at risk of fading.
Managing these challenges is vital to ensuring Starlink fulfills its mission without compromising our planet or our relationship with the stars.
Navigating the Regulatory Maze
SpaceX’s Starlink initiative also faces mounting regulatory hurdles. Here are some of the challenges:
- Spectrum Allocation
Starlink’s global footprint requires frequencies that are highly competitive. Sharing bandwidth with other satellite operators creates a logistical and political balancing act.
- National Jurisdictions
Each country enforces unique regulations to oversee satellite operations. Gaining approvals for Starlinks in specific territories is both time-consuming and politically fraught.
- Orbital Regulation
Governing bodies like the FCC and ITU must enforce stricter rules to mitigate overcrowding in orbit, which complicates SpaceX’s expansion plans.
Regulatory compliance is a persistent challenge, yet it’s vital for SpaceX to address these issues responsibly to maintain public and governmental trust.

A Look Ahead: SpaceX’s Ambitions for Starlinks
The latest launch is part of SpaceX’s larger strategy to expand its constellation to over 42,000 satellites in the coming years. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
- Enhanced Laser Links
SpaceX plans to improve satellite communication systems, increasing their coverage and performance for users.
- Scaled Global Coverage
While Starlink is concentrated in specific regions, the goal remains full global service availability, especially in underserved markets.
- Lower Costs
SpaceX continually works to reduce customer hardware costs, making the service financially accessible to a broader demographic.

Starlink’s Bright Future Shrouded in Uncertainty
Starlink represents the epitome of human ingenuity, aiming to bridge the digital divide for millions. Its innovative design and transformational benefits are hard to ignore, but so are the environmental and regulatory questions it raises. SpaceX’s challenge is to responsibly build this venture while addressing the legitimate concerns of scientists, regulators, and advocates.
At its best, Starlink could revolutionize how we connect, learn, and innovate worldwide. At its worst, it could irreversibly impact the very environment it operates in.
For now, one thing is certain: the Starlink story is still being written.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Starlink
1. What is Starlink?
Starlink is SpaceX’s ambitious project aimed at providing global high-speed internet access through a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. Designed to improve connectivity in underserved and remote areas, Starlink offers faster internet speeds and lower latency compared to traditional satellite internet.
2. How does Starlink work?
Starlink satellites beam internet signals directly to user terminals (antennas) placed on Earth. These satellites are equipped with advanced phased-array antennas and, in newer models, inter-satellite laser links that improve data relay by allowing satellites to communicate directly with one another. This technology reduces reliance on ground stations and provides a faster and more consistent connection.
3. What are the key benefits of Starlink?
- Improved Connectivity: Ideal for rural and remote areas that lack traditional infrastructure.
- Emergency Response: Portable terminals enable communication during disasters.
- Low Latency: Its low Earth orbit allows for faster real-time applications like gaming and video calls.
- Economic Empowerment: Enables startups and local businesses in underserved areas to thrive.
4. Are there any environmental concerns with Starlink?
Yes, Starlink has raised concerns, including:
- Space Debris: Thousands of satellites in orbit elevate the risk of collisions and debris.
- Astronomical Impact: Satellite reflections interfere with astronomical observations.
- Light Pollution: Visible satellite trails disrupt natural night sky views.
SpaceX is working on mitigating these concerns, such as using non-reflective coatings and ensuring satellites are deorbited responsibly at the end of their lifecycle.
5. Is Starlink available in my region?
Starlink currently has coverage in many parts of the world, with ongoing plans to expand its reach globally. To check availability in your region, visit Starlink’s official website and enter your address.
6. How much does Starlink cost?
The cost of Starlinks includes a one-time fee for the user terminal and a monthly subscription for internet access. SpaceX has stated its commitment to reducing hardware costs over time to make the service more accessible to a broader audience.